Introduction to Fabrication in Welding
What is welding fabrication? Read our guide on the importance of fabrication in welding and how UTI can help you learn this in-demand skill!
Key Points
There are a number of tools and kinds of equipment a welder has to have to complete a task successfully.
The right instruments allow a welder to complete the process of molding metals and other materials together to form new shapes. Heat, pressure and filler material are applied during the process of welding. It’s important that the tools being used can handle the work that’s being done.
The metal inert gas (MIG) welding torch tip is composed of different consumable parts. The end of a welding torch, also known as a welding nozzle, is one of these, and something that a welder cannot be without. The welding nozzle directs gas into the weld puddle and protects the contact tip from molten metal.
Different nozzles exist and a torch can be fitted for certain types to accomplish desired results and effects. Keep on reading to find out more about the various kinds.
MIG nozzles direct the shielding gas into the weld puddle and help protect it from contamination. MIG welding (sometimes referred to as gas metal arc welding, or GMAW) is a process that requires the use of a nozzle, as it uses a shielding gas. When talking about welding nozzles, it’s important to understand the type of joint to be welded to make sure the weld has the appropriate gas coverage.
The types of MIG welding nozzles on the market are available in a range of sizes and shapes. Choosing one will depend on what the application is, the welding process that is being used and joint access. Typically, you can get nozzles in slip-on or thread-on varieties, as well as heavy-duty or standard styles.
Heavy-duty nozzles are going to be thicker in construction and have more insulation than standard nozzles. This makes them fit for jobs that are between 400 and 600 amperages. Standard nozzles with thinner walls are more suited for 100- to 300-amp applications.
When it comes to choosing threaded or slip-on nozzles, it will likely depend on the type of MIG welding gun you have, as some can only accommodate one or the other. Threaded nozzles will connect more securely to the torch, which helps prevent gas from leaking. One potential downside is that they can be hard to remove.
Slip-on welding nozzles are quicker and easier to remove. They are typically better suited for overhead welds and can be lower priced than threaded nozzles. However, the nozzle can sometimes become displaced and cause things to sit off-center.
Whether the nozzles you choose are threaded or slip-on, there are some different nozzle shapes to choose from that will affect the welds being worked on. These include:

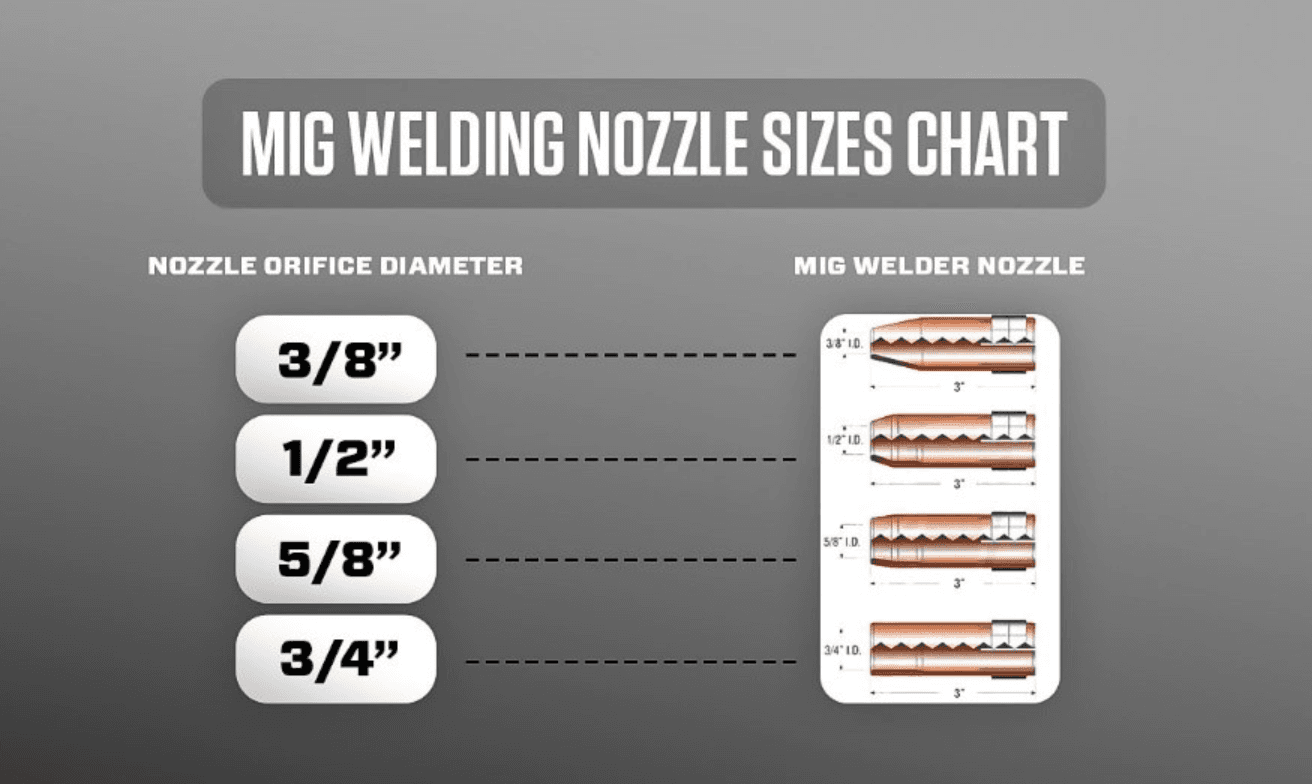
The sizes for MIG welding nozzles can vary, with bottleform and conical nozzles available from 3/8 of an inch up to 7/8 of an inch. Cylindrical/straight nozzles are usually available only in larger bore sizes.
When choosing a nozzle size, using the largest bore size possible is best since it helps to optimize gas coverage during a weld. It also helps lower the chances of spatter buildup that can cause porosity.
Make sure you don’t choose a nozzle so large that it compromises your accessibility to the workpiece or welding joint.
Just like there are choices when it comes to MIG welding nozzle types, sizes and durability levels, there is also some variety when it comes to materials. Some of these include:
When it comes to all welding gear and equipment, something to keep in mind is proper storage and maintenance. Taking care of MIG welding nozzles will ensure they last longer and deliver peak performance.
MIG welding nozzles should be stored in their original packaging, which is usually a small plastic bag. Keeping them separated from each other and other equipment will ensure they stay free from dents or scratches. When handling nozzles, wearing gloves can help prevent contaminants from adhering to them.
Some welders use MIG welding nozzle gel – a protective substance that prevents spatter buildup on the welding nozzle and contact tip. By applying the gel, welders can maintain a cleaner nozzle, which helps ensure consistent gas flow and improves the overall quality of the weld.
Regardless, it’s still best practice to clean MIG nozzles regularly to protect the weld puddle from dirt or other debris. Inspecting nozzles for spatter buildup and cleaning them using recommended tools or with an anti-spatter compound is the best way to keep them looking and performing great.
A MIG spot weld nozzle is specifically designed for concentrating the heat on a smaller area, allowing for precise welds. Unlike a regular MIG welding nozzle, which distributes gas evenly for general welding tasks, the spot weld nozzle has a narrower tip to focus the gas flow and arc on a specific location.
Copper is generally considered the best material for MIG welder nozzles due to its excellent thermal conductivity and durability. It withstands high temperatures and resists spatter buildup, making it ideal for consistent performance.
How often you change your MIG welding nozzle depends on the intensity and duration of use. Inspect the nozzle after every major project or if you notice spatter buildup, wear or reduced gas flow.
If the process of MIG welding and MIG welding nozzles interest you, why not pursue a career doing it? The Welding Technology program at Universal Technical Institute (UTI) allows students to learn MIG welding techniques as well as other major welding types.
In the 9- to 10-month program, students learn all about the procedures and equipment used in MIG welding, as well as shielded metal arc welding (SMAW), flux-cored arc welding (FCAW) and gas tungsten arc welding (GTAW). By the time they graduate, students will be prepared with the hands-on training and skills needed to pursue a career in a growing industry.1
Learn more by requesting information from an Admissions Representative today.
Universal Technical Institute of Illinois, Inc. is approved by the Division of Private Business and Vocational Schools of the Illinois Board of Higher Education.